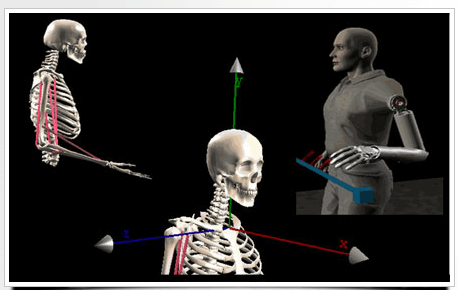
MSMS Musculoskeletal Modeling Software – MSMS
MSMS is still available for download and in active use in many labs but we are not able to provide user support at this time.
Publications
Tsianos, G. A., & Loeb, G. E. (2022). Physiology and computational principles of muscle force generation. In Encyclopedia of Computational Neuroscience (pp. 2779-2795): Springer.
Nagamori, A., Laine, C. M., Loeb, G. E., Valero-Cuevas, F. J. Force variability is mostly not motor noise: Theoretical implications for motor control. PLoS Comp Biol. 2021;17(3):e1008707.
Tsianos, G.A. and Loeb, G.E. Muscle and limb mechanics Comprehensive Physiology, 7:429-462, 2017.
Jalaleddini, K., Niu, C., Chakravarthi Raja, S., Sohn, W.J., Loeb, G.E., Sanger, T., and Valero-Cuevas, F. Neuromorphic meets neuromechanics, Part II: The role of fusimotor drive J. Neural Eng., at press dx.doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aa59bd, 2017.
Loeb, G.E. and Tsianos, G.A. Major remaining gaps in models of sensorimotor systems Front. Comput. Neurosci. dx.doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2015.00070, 2015.
Loeb, G.E. and Mileusnic, M. Proprioceptors and models of transduction Scholarpedia, 10(5):12390, 2015.
Loeb, G.E. and Davoodi, R. Musculoskeletal mechanics and modeling Scholarpedia, 2015.
Tsianos, G.A. Goodner, J. and Loeb, G.E., Useful properties of spinal circuits for learning and performing planar reaches J. Neural Eng. 11 (2014) 056006 (21pp), doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/11/5/056006, 2014.
Loeb, G.E. Spinal Cord, Integrated (Non CPG) Models of Encyc Comp Neurosci DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4614-7320-6_648-1, 2014.
Tsianos, G.A. and Loeb, G.E. Muscle Physiology and Modeling www.scholarpedia.org/article/Muscle Physiology and Modeling Scholarpedia, 8(10):12388 doi:10.4249, 2013.
De Rugy, A., Loeb, G.E. and Carroll, T.J. Are muscle synergies useful for neural control? Front. Comput. Neurosci., DOI: 10.3389, 2013.
De Rugy, A., Loeb, G.E. and Carroll, T.J. Virtual biomechanics: a new method for online reconstruction of force from EMG recordings. J. Neurophysiol., 108(12): 3333-3341, 2012.
Davoodi, R. and Loeb, G.E., Development of a physics-based target shooting game to train amputee users of multijoint upper limb prostheses. Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, 21:85-95, 2012.
Li, Y., Smith, L.H., Hargrove, L.J., Weber, D.J., and Loeb, G.E. Sparse Optimal Motor Estimation (SOME) for Extracting Commands for Prosthetic Limbs. IEEE Trans. Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 10.1109TNSRE.2012.2218286, 2012.
Li, Y., Levine, W.S., and Loeb, G.E. A Two-Joint Human Posture Control Model With Realistic Neural Delays. IEEE Trans. Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 20:738-748, 2012.
Tsianos, G.A., Rustin, C. and Loeb, G.E. Mammalian muscle model for predicting force and energetics during physiological behaviors. IEEE Trans. Neural Systems & Rehab. Engng. 2:117-133, 2012.
Davoodi, R. and Loeb, G.E. Real-time animation software for customized training to use motor prosthetic systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 20:134-142, 2012.
Davoodi, R. and Loeb, G.E. MSMS Software for VR Simulations of Neural Prostheses and Patient Training and Rehabilitation. Stud. Health Technol. Inform., 163:156-162, 2011.
Mileusnic, M.P., and Loeb, G.E. Force estimation from ensembles of Golgi tendon organs. J. Neural Eng. 6:1-15, 2009.
Cheng, E.J. and Loeb, G.E. On the Use of Musculoskeletal Models to Interpret Motor Control Strategies from Performance Data. Journal Neural Engineering 5:232-253, 2008.
Song, D., Lan, N., Loeb, G.E. and Gordon, J. Model-based sensorimotor integration for multi-joint control: Development of a virtual arm model. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 36(6):1033–1048, 2008.
Song, D., Raphael, G. Lan, N. and Loeb, G.E. Computationally Efficient Models of Neuromuscular Recruitment and Mechanics. Journal of Neural Engineering. 5:175-184, 2008.
Hauschild, M., Davoodi, R. and Loeb, G.E. A Virtual Reality Environment for Designing and Fitting Neural Prosthetic Limbs. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and rehabilitation Engineering, 15(1):9-15, 2007.
Davoodi, R., Urata, C., Hauschild, M., Khachani, M., Loeb, G.E. Model-Based Development of Neural Prostheses for Movement. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 54:11):1909-1918, 2007.
Mileusnic,M.P., Brown,I.E., Lan,N. and Loeb,G.E. Mathematical models of proprioceptors: I. Control and transduction in the muscle spindle. J Neurophysiol. 96:1772-1788, 2006.
Mileusnic,M.P. and Loeb,G.E. Mathematical models of proprioceptors: II. Structure and function of the Golgi tendon organ. J Neurophysiol. 96: 1789-1802, 2006.
Loeb, G.E. and Davoodi, R. The Functional Reanimation of Paralyzed Limbs. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag., 24(5):45-51, 2005.
Davoodi R, Brown, I.E. and Loeb, G.E. Advanced modeling environment for developing and testing FES control systems. Med Engng& Physics 25:3-9, 2003.
Dupont Salter, A.-C., Richmond, F.J.R. and Loeb, G.E. Effects of Muscle Immobilization at Different Lengths on Tetrodotoxin-induced Disuse Atrophy. IEEE Trans. Neural Sys. Rehab. Engng., 11:209-217, 2003.
Dupont Salter, A.-C., Richmond, F.J.R. and Loeb, G.E. Prevention of Muscle Disuse Atrophy by Low-frequency Electrical Stimulation in Rats. IEEE Trans. Neural Sys. Rehab. Engng., 11:218-226, 2003.
Davoodi, R. and Loeb, G.E. A Software Tool for Faster Development of Complex Models of Musculoskeletal Systems and Sensorimotor Controllers in Simulink. J. Appl. Biomech. 18:357-365, 2002.
Loeb, G.E., Brown, I.E., Lan, N. and Davoodi, R. The importance of biomechanics. Adv. Exper. Med. Biol.508: 481-487, 2002.
Dupont, A.-C., Sauerbrei, E. E., Fenton, P. V., Shragge, P. C., Loeb, G. E. and Richmond, F. J. R. Real-Time Sonography to Estimate Muscle Thickness: Comparison with MRI and CT. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound, 29(4):230-236, 2001.
Corneil, B.D.,Olivier, E., Richmond, F.J.R., Loeb, G.E. and Munoz, D.P. Neck Muscles in the Rhesus Monkey. II. Electromyographic Patterns of Activation Underlying Postures and Movements. J. Neurophysiol, 86:1729-1749, 2001.
Loeb, G.E. Learning from the Spinal Cord. J. Physiol. (London), 533:111-117, 2001.
Brown, I.E. and Loeb, G.E. A reductionist approach to creating and using neuromusculoskeletal models. Chapter in: Biomechanics and Neuro-Control of Posture and Movement, (Eds.) J. Winters and P. Crago, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2000, pp 148-163.
Brown, I.E. and Loeb, G.E. Measured and modeled properties of mammalian skeletal muscle: III. The effects of stimulus frequency on stretch-induced force enhancement and shortening-induced force depression. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motility, 21:21-31, 2000.
Brown, I.E. and Loeb, G.E. Measured and modeled properties of mammalian skeletal muscle: IV. The dynamics of activation and deactivation. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motility, 21:33-47, 2000.
Cheng, E., Brown, I.E. and Loeb, G.E. Virtual Muscle: A computational approach to understanding the effects of muscle properties on motor control. J. Neurosci. Methods, 101:117-130, 2000.
Loeb, G.E. Overcomplete Musculature or Underspecified Tasks? Motor Control, 4:81-83, 2000.
Singh, K., Richmond, F.J.R. and Loeb, G.E. Recruitment Properties of Intramuscular and Nerve-trunk Stimulating Electrodes. IEEE-Trans. Rehab. Engng., 83(3):276-285, 2000.
Brown, I.E. and Loeb, G.E. Measured and modeled properties of mammalian skeletal muscle: I. The effects of post-activation potentiation on the time-course and velocity dependencies of force production. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motility, 20:443-456, 1999.
Brown, I.E., Cheng, E.J. and Loeb, G.E. Measured and modeled properties of mammalian skeletal muscle: II. The effects of stimulus frequency on force-length and force-velocity relationships. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motility 20:627-643, 1999
Loeb, G.E, Brown, I.E and Cheng, E. A hierarchical foundation for models of sensorimotor control. Exp. Brain Res.126: 1-18, 1999.
Brown, I.E., Kim, D.H. and Loeb, G.E. The effect of sarcomere length on triad location in intact feline caudofemoralis muscle fibers. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motility, 19:473-477, 1998.
Brown, I.E., Satoda, T., Richmond, F.J.R. and Loeb, G.E. Feline caudofemoralis muscle: Muscle fiber properties, architecture and motor innervation. Exp. Brain Res. 121:76-91, 1998.
Brown, I.E. and Loeb, G.E. Post-activation potentiation – a clue for simplifying models of muscle dynamics. Amer. Zool. 38:743-754, 1998.
Brown, I.E., Scott, S.H. and Loeb, G.E. Mechanics of feline soleus: II. Design and validation of a mathematical model. J. Muscle Research and Cell Motility 17:221-233, 1996.
Brown, I.E., Liinamaa, T.L. and Loeb, G.E. Relationships between range of motion, Lo and passive force in five strap-like muscles of the feline hindlimb. J. Morph. 230:69-77, 1996.
Scott, S.H., Brown, I.E. and Loeb, G.E. Mechanics of feline soleus: I. Effect of fascicle length and velocity on force output. J. Muscle Research and Cell Motility 17:205-218, 1996.
Loeb, G.E. What can we expect from models of motor control? Behav. & Brain Sci., 18(4):767-768, 1995.
Scott, S.H. and Loeb, G.E. Mechanical properties of the aponeurosis and tendon of the cat soleus muscle during whole-muscle isometric contractions. J. Morph. 224:73-86, 1995.
Scott, S.H., Engstrom C.M. and Loeb, G.E. Morphometry of human thigh muscles. Determination of fascicle architecture from magnetic resonance imaging. J. Anat.182:249-257, 1993.
Young, R.P., Scott, S.H. and Loeb, G.E. The distal hindlimb musculature of the cat: Multiaxis moment arms at the ankle joint. Exp. Brain Res. 96:141-151, 1993.
Blaszczyk, J. and Loeb, G.E. Why Cats Pace on the Treadmill. Physiol. & Behav., 53:501-507, 1993.
Heckman, C.J., Weytjens, J.L.F. and Loeb, G.E. Effect of velocity and mechanical history on the forces of motor units in the cat medial gastrocnemius muscle. J. Neurophysiol. 68:1503-1515, 1992.
Loeb, G.E. Past the equilibrium point. Behav. & Brain Sci., 15:774-775, 1992.
Scott, S.H., Thomson, D.B., Richmond, F.J.R. and Loeb, G.E. Neuromuscular organization of feline anterior sartorius: II. Intramuscular length changes and complex length-tension relationships during stimulation of individual nerve branches. J. Morph. 213:171-183, 1992.
Young, R.P., Scott, S.H. and Loeb, G.E. An intrinsic mechanism to stabilize posture – joint-angle-dependent moment arms of the feline ankle muscles. Neurosci. Lett. 145:137-140, 1992.
He, Jiping, Levine, W.S. and Loeb, G.E. Feedback gains for correcting small perturbations to standing posture. IEEE Trans on Automatic Control, 36:322-332, 1991.
Chanaud, C.M., Pratt, C.A. and Loeb, G.E. Functionally Complex Muscles of the Cat Hindlimb. II. Mechanical and Architectural Heterogeneity Within the Biceps Femoris. Experimental Brain Research, 85:257-270, 1991.
Chanaud, C.M., Pratt, C.A. and Loeb, G.E. Functionally Complex Muscles of the Cat Hindlimb. V. The Roles of Histochemical Fiber-type Regionalization and Mechanical Heterogeneity in Differential Muscle Activation. Experimental Brain Research, 85:300-313, 1991.
Engstrom, C.M., Loeb, G.E., Reid, J.G., Forrest, W.J. and Avruch, L. Morphometry of the Human Thigh Muscles. A Comparison Between Anatomic Sections and Computer Tomographic and Magnetic Resonance Images. J. Anat., 176:139-156, 1991.
Gordon, D.C., Loeb, G.E. and Richmond, F.J.R. Distribution of Motoneurons Supplying Cat Sartorius and Tensor Fasciae Latae, Demonstrated by Retrograde Multiple-labeling Methods. J. Comp. Neurol., 304:357-373, 1991.
He, J., Levine, W.S. and Loeb, G.E. Feedback Gains for Correcting Small Perturbations to Standing Posture. IEEE Trans. on Automatic Control, 36:322-332, 1991.
Pratt, C.A., and Loeb, G.E. Functionally Complex Muscles of the Cat Hindlimb. I. Patterns of Activation Across Sartorius. Experimental Brain Research, 85:243-256, 1991.
Pratt, C.A., Chanaud, C.M. and Loeb, G.E. Functionally Complex Muscles of the Cat Hindlimb. IV. Intramuscular Distribution of Movement Command Signals and Cutaneous Reflexes in Broad Bifunctional Thigh Muscles. Experimental Brain Research, 85:281-299, 1991.
Gans, C., Loeb, G.E. and de Vree, F. Architecture and consequent physiological properties of the semitendinosus muscle in domestic goats. J. Morphology, 199:287-297, 1989.
Loeb, G.E. and Richmond, F.J.R. Motor partitioning: Epiphenomena masquerading as control theory. Behav. & Brain Sci., 12:660-661, 1989.
Loeb, G.E., He, J. and Levine, W.S. Spinal Cord Circuits: Are They Mirrors of Musculoskeletal Mechanics? J. Motor Behavior, 21:473-491.
Loeb, G.E., Pratt, C.A., Chanaud, C.M. and Richmond, F.J.R. Distribution and innervation of short, interdigitated muscle fibers in parallel-fibered muscles of the cat hindlimb. J. Morph. 191:1-15, 1987.
Channaud, C.M., Pratt, C.A. and Loeb, G.E. A Multiple-contact EMG Recording Array for Mapping Single Muscle Unit Territories. J. Neurosci. Meth., 21:105:112, 1987.
Loeb, G.E. Restoring Motor Function through Electrical Stimulation. MS Quart. Rep., 6:47-50, 1987.